Ocean deserts: Effects of climate change on marine ecosystems - Science Week Special.
This years Science Week by Science Foundation Ireland (SFI) runs from 10-17th of November and the theme for this year is Climate Action, seeking to help people understand climate change, how science and technology can help us create a positive climate future and the impact we as individuals can have on climate change. To raise awareness we have composed a special short article on the effects of climate change on marine ecosystems.
So how is climate change affecting marine ecosystems around the world and what is getting hit hardest? We all know the Arctic sea ice is melting but how are the tropics and temperate seas coping with these extremes in climatic perturbations?
A new study
published in the journal Nature
has shown that local populations of fish, mollusks and other marine animals are disappearing at twice the rate of land-based species. Of the marine species they studied, 56 percent experienced a range contraction due to global warming, compared to 27 percent of the land species.
Marine organisms especially those that live in shallower water near the coasts, are much more vulnerable to global warming than land animals. Species like fish, crabs and lobster are already more likely to be living near the threshold of life-threatening temperatures, and because in the ocean, there are fewer places to hide from extreme heat.
"We already know terrestrial species are highly vulnerable to climate change," he said, "and now we see that marine species are even more vulnerable.", said lead author of the research paper, Malin Pinsky.
Some fish species can shift their distribution or ranges poleward to cooler waters, but others, those thermal refuges will be inaccessible because the cooler areas are too far away or because shallow water habitat along continental shelves is not continuous. This could affect people in developing countries which rely heavily on fish as a daily source of nutrients, thus, understanding which species are most at risk allows scientists and fisheries managers to better allocate resources for conservation.
Reaching Thermal Limits:
Ten percent of the world's population depends on fisheries for their livelihoods, and 4.3 billion people are reliant on fish for 15 percent of their animal protein intake. This new study shows that some of those species close to the equator are among the most vulnerable to global warming because they already live near the edge of their heat tolerance.
For example, off the coast of North Carolina, U.S., summer flounder have moved far north to find cooler waters that it's had a big effect on fisheries, with boats having to travel more than 600 miles farther north to catch the species.
Another study
has suggested that the limited phenotypic plasticity
of cold-adapted species such as Atlantic cod ( Gadus morhua
) L. will cause distributions to shift toward the poles in response to rising sea temperatures. Some cod stocks are predicted to collapse, and the studies direct observations of habitat occupation suggested that adult cod will be able to tolerate warming seas, but that climate change will affect cod populations at earlier life-history stages as well as exerting effects on cod prey species.
Atlantic Cod ( Gadus morhua ). PHOTO: HANS HILLEWAERT VIA WIKIMEDIA COMMONS
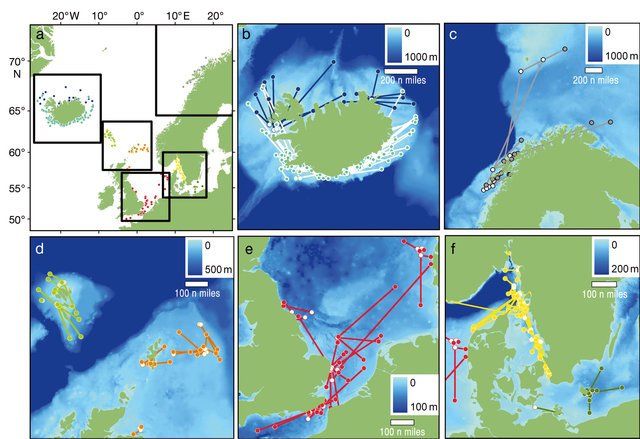
Using electronic tags to measure the thermal niches of Atlantic cod from 8 different locations across the northeast Atlantic, they found that their total thermal niche ranged from -1.5 to 19 degrees C; this range was narrower (1 to 8 degrees C) during the spawning season.
Area of study and Gadus morhua tagging locations. Photo: Righton et al ., 2010.
At the extreme ends of Atlantic cod's range, they eat less and are smaller. Also, warmer temperatures can cause the fish to mature slower and to spawn earlier.
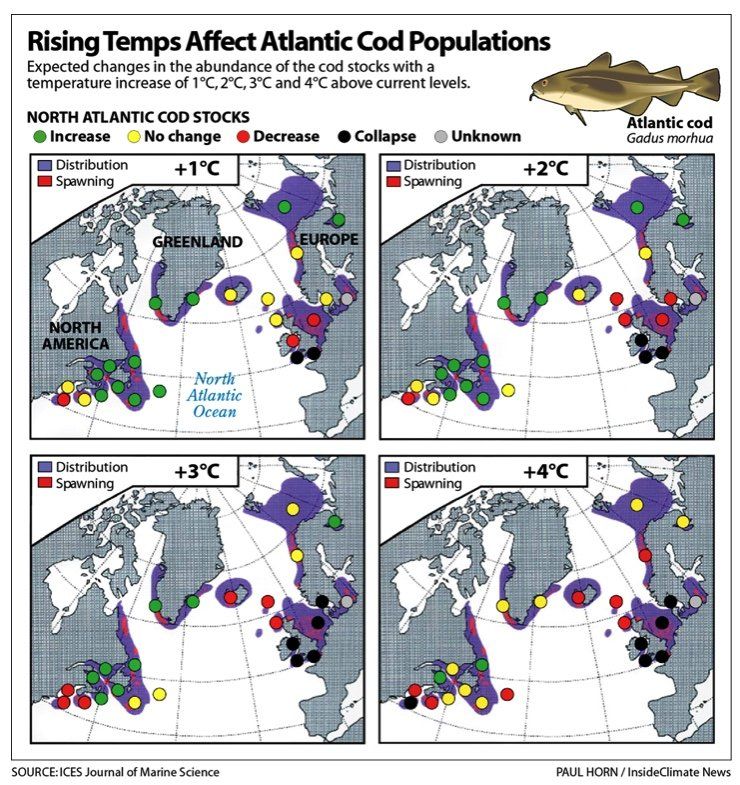
A study published in the ICES Journal of Marine Sciences
in 2005 looked at how cod populations would be impacted by global warming. It found that as the Atlantic warms, some would decline or disappear, while others would increase.
Ocean Heatwaves:
A recent report by the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC)
has declared oceans are increasingly taking the heat from climate change and points to a problem scientists are growing more concerned about: marine heat waves.
There is an abundance of robust scientific evidence that shows that extreme heat events on land are getting worse as climate change accelerates. However, land dwellers aren’t the only ones feeling the heat. A growing body of evidence is showing similar events underwater, when the seas experience periods of unusually warm temperatures.
Over a 100 scientists from over 30 different countries contributed to the study, called the Special Report on the Ocean and Cryosphere in a Changing Climate. The report found that the frequency of heat waves in oceans has very likely doubled since 1982. Climate impacts are projected to cause greater impacts in the coming years. By 2081, the frequency of these extreme heat events could jump by 20 to 50 times, depending on how successful the world is at cutting down on the greenhouse gas emissions causing rising temperatures on our planet. In a scenario with continued high emissions, those underwater extreme heat events could become ten times more intense.
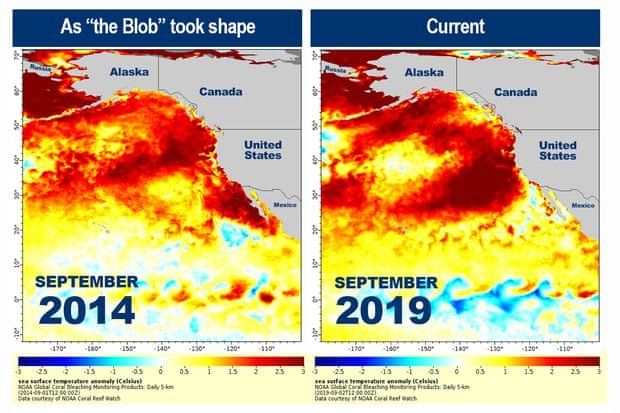
The ocean off the western coast of North America is five degrees Fahrenheit hotter than usual after warming at an unusually rapid rate, according to the US National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA).
Marine heatwaves are defined as oceanic events in which the surface temperature of the water is warmer than 90% of past measurements for at least five days in a row. The heatwave I n September 2019 was the second-largest since scientists started tracking the phenomenon in 1981. In 2014-2016, it created toxic algae blooms, and killed seal lions and endangered whales by forcing them to forage closer to shore. The direct cause of the heat is weak winds, though these conditions do not usually persist for months at a time as they have done this year.
Temperatures higher than normal are marked in orange and red. Photograph source: NOAA.
Ocean Deserts:
One of the signatures of global warming is rising ocean temperatures. As the surface layer of the ocean warms, the water becomes less dense and stays on top rather than mixing down to allow cooler, nutrient-rich water to well up. Over time, areas with less mixing show reduced productivity, less phytoplankton, and so less chlorophyll. This is ocean desertification.
Researchers at NASA's Ocean Biology Distributed Active Archive Center (OB.DAAC) at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, used surface chlorophyll data to locate areas where low-chlorophyll regions were expanding during their nine-year time series of data. The team also used sea surface temperature data from the Advanced Very High Resolution Radiometer (AVHRR), available at NASA's Physical Oceanography DAAC (PO.DAAC).
While many abiotic and biotic factors can reduce ecosystem productivity—overfishing, for example, or El Niño, a cyclic condition characterised by higher-than-normal sea surface temperatures—global warming is expected to result in particularly large reductions in productivity. Studies predict that if global warming intensifies, areas with decreasing chlorophyll will match up with areas of increasing sea surface temperature.
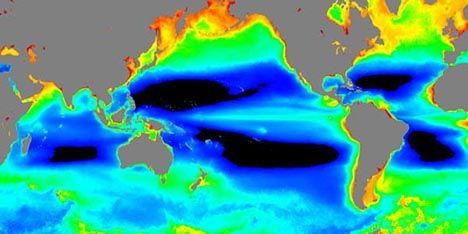
The research team led by Jeffrey Polovina looked at the North Atlantic, the South Atlantic, the Indian Ocean—and saw the same trends all over the globe. Over nearly the past decade, regions with low surface chlorophyll were expanding into nearby ocean basins. The total area lost was quite enormous. The area of new global ocean desert added up to 6.6 million square kilometers (2.5 million square miles), representing about a 15 percent expansion in the area of the least productive waters between 1998 and 2006. In addition, the expansion of low-productivity waters matched up with significant increases in sea surface temperature.
Those black areas are the least productive 'desert' regions of the oceans. Image: NOAA
- © Ocean Research & Conservation Ireland (ORCireland) and www.orcireland.ie , est. 2017. Unauthorized use and/or duplication of this material without express and written permission from this site’s author and/or owner is strictly prohibited. Excerpts and links may be used, provided that full and clear credit is given to Ocean Research & Conservation Ireland and www.orcireland.ie with appropriate and specific direction to the original content.
References
:
Polovina, J., E. Howell,and M. Abécassis. 2008. Ocean’s least productive waters are expanding. Geophysical Research Letters
35, L03618, doi: 10.1029/2007GL031745.
Pinsky, M.L., Eikeset, A.M., McCauley, D.J. et al. Greater vulnerability to warming of marine versus terrestrial ectotherms. Nature 569, 108–111 (2019) doi:10.1038/s41586-019-1132-4.
Righton, David & Andersen, Ken & Neat, Francis & Thorsteinsson, & Steingrund, & Svedäng, Henrik & Michalsen, Kathrine & Hinrichsen, & Bendall, & Neuenfeldt, Stefan & Wright, Peter & Jonsson, & Huse, Geir & van der Kooij, Jeroen & Mosegaard, Henrik & Hüssy, Karin & Metcalfe, J.. (2010). Thermal niche of Atlantic cod Gadus morhua: Limits, tolerance and optima. Marine Ecology Progress Series. 420. 1-13. 10.3354/meps08889.
SHARE THIS ARTICLE